How to Select the Right Elastomer for Your Sealing Boots and Fasteners
Elastomers are the key to providing effective sealing solutions for applications in outdoor, marine, medical and any environment where sealing stuff in or sealing stuff out is imperative. Elastomers are versatile materials typically composed of polymers, and manufacturers prize them for their ability to bend and stretch in a variety of ways before returning to their original shape.
However, not all elastomers are the same. Elastomers can incorporate a wide range of designs and materials depending on the needs of their intended application. More than 20 different types of standard elastomers exist, and each possesses unique functions in both process equipment and finished products.
Different elastomer formulations affect the physical properties, functions, and service life of your components and systems. This is why it’s essential to test a few different elastomers to determine the best one for your needs. In this post, we outline ways to evaluate elastomers for their capacity to perform well in your application, and we also describe some of the best uses of each different type of elastomer.
Questions to Ask When Selecting an Elastomer
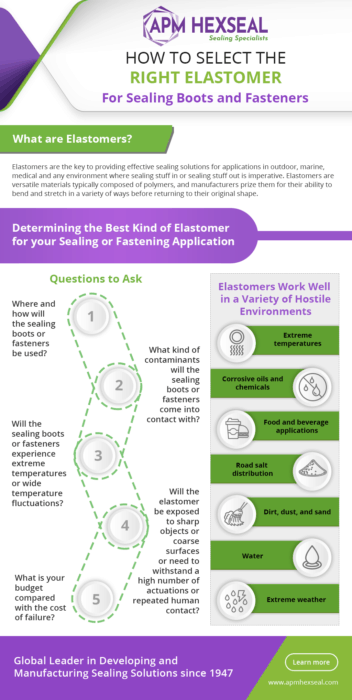
When you’re trying to determine the best kind of elastomer to use for your sealing or fastening application, keep the following few questions in mind:
- Where and how will the sealing boots or fasteners be used? Applications that use elastomers can appear in many different environments, such as:
- Outdoor
- Marine
- Industrial/manufacturing environments
- Drilling and downhole
- Food and beverage (some elastomers have FDA approval; others don’t)
- Aerospace
- Construction
- Medical
- What kind of contaminants will the sealing boots or fasteners come into contact with?
- Different elastomers hold up better against specific environmental conditions or contaminants.
- Will the sealing boots or fasteners experience extreme temperatures or wide temperature fluctuations?
- Will the elastomer be exposed to sharp objects or coarse surfaces or need to withstand a high number of actuations or repeated human contact?
- What is your budget compared with the cost of failure?
Elastomer Selection Criteria
It is vital to choose an elastomer that meets the demands of the given application. The right product will enhance the longevity and overall performance of sealing boots and fasteners.
The following criteria can help users achieve superior durability and functionality.
Temperature Capabilities
- Low-Temperature Concerns. Elastomers become less flexible at low temperatures, hardening and leading to cracks in the seal.
- High-Temperature Concerns. Irreversible chemical changes caused by exposure to heat can lead to reduced compression resistance and increased rigidity in elastomers.
Fluid Compatibility
The reaction an elastomer has to a fluid can vary. For example, compatibility with hydrocarbons, alcohols, acids, and other substances differs significantly across elastomer types. The following factors must be considered to ensure the selected elastomer performs as expected without rapid deterioration:
- Chemical Concentration
- Operating Temperature
- System Pressure
Abrasion and Tear Resistance
It is crucial to use a dynamic seal in applications subject to friction and movement. Elastomers such as Aflas and HNBR offer excellent abrasion resistance. Special compounding in carboxylated nitrile seals also enables enhanced abrasion resistance.
Differential Pressure Resistance
Elastomers must be capable of accommodating potential pressure changes to avoid seal failure.
Cost-Effectiveness
Cost is typically the deciding factor when choosing the right part, assuming functional requirements have been met. Price variations can be attributed to differences in processing and compounding.
Common Elastomer Types
There are many types of elastomers on the market, each offering unique advantages and properties. Understanding the differences can help users make informed decisions relating to the specific challenges of an application, whether dealing with aggressive chemicals or high temperatures.
Common types of elastomers include:
Ethylene Propylene (EPDM)
- Key Features. Offers superior resistance to alcohols, steam, water, and glycol-based coolants.
- Applications. Often used in outdoor applications and automotive cooling systems due to its weather-resistant properties
- Temperature Range. Effective within a range of -65 F to +300 F
- Limitations. Not suitable for use with fuels and other petroleum-based fluids
Nitrile
- Key Features. Low-temperature flexibility with excellent resistance to fuels and petroleum-based oils
- Applications. Commonly used in aeronautical and automotive industries for oil and fuel handling systems
- Temperature Range. Effective within a range of -65 F to +250 F
- Limitations. Exhibits poor resistance to sunlight, ozone, and other weathering conditions due to the unsaturated carbon bonds in its polymer structure
Hydrogenated Nitrile (HNBR)
- Key Features. Maintains chemical stability and provides enhanced strength, even in harsh environments
- Applications. Best suited for oil field exploration, automotive timing belts, and other high mechanical stress environments
- Temperature Range. Serviceable within a range of -40 F to +325 F
- Advantages. Improved chemical and heat resistance compared to Nitrile
Polyacrylate
- Key Features. Ideal for exterior applications due to its excellent resistance to ozone and UV light
- Applications. Commonly used in seals for power steering systems and automobile transmissions
- Temperature Range. Functional between -20 F and +350 F
- Limitations. Not advisable for dynamic sealing due to poor abrasion resistance
Neoprene
- Key Features. Offers good weather resistance and moderate resistance to petroleum oils, balancing cost-effectiveness with performance
- Applications. Refrigeration seals and HVAC systems
- Temperature Range. -65 F and +212 F
- Properties. Moderate oil resistance and good flame resistance
Fluorocarbon
- Key Features. Extremely resistant to chemicals and high temperatures
- Applications. Seals for chemical processing plants and aerospace fuel systems
- Temperature Range. Capable of handling continuous service between -20 F and +400 F, with intermittent exposure to temperatures up to 500 F
- Advantages. Replaces nitriles in applications demanding superior chemical resistance
Silicone
- Key Features. Excellent low-temperature flexibility with the broadest temperature range of all elastomers
- Applications. High-temperature automotive gaskets to kitchenware
- Temperature Range. Operates efficiently between -80 F and +400 F
- Limitations. Generally used in static applications due to its poor abrasion and tear resistance
Aflas
- Key Features. Resistant to acids, steam, bases, and other extreme conditions
- Applications. Chemical processing and oil/gas extraction
- Temperature Range. Can withstand temperatures from -10 F to +400 F
- Advantages. Excellent option for high-temperature and high-pressure environments
Fluorosilicone
- Key Features. Enhances chemical resistance by merging the best properties of fluorocarbon with silicone.
- Applications. Commonly used in aerospace and military applications for oil and fuel contact in extreme environments.
- Temperature Range. Functional between -80 F and +350 F
- Limitations. Similar to silicone, it is typically limited to static sealing, offering poor abrasion resistance
Top-Quality Elastomer Sealing Solutions from APM Hexseal
Building quality sealing boots or fasteners involves accounting for many variables. Fortunately, we at APM Hexseal bring years of experience to the elastomer design process, helping customers across the globe find ways to get the most from their elastomer options.
We’ve compiled our extensive experience from working with elastomers into our eBook, “Elastomer Shlastomer, Right?”, which is available for download here. If you would like to learn more about our full selection of products and services, contact us today and Ask the Experts at APM Hexseal.